Introduction:
GST ITC Setoff Rules Navigating the labyrinth of Tax regulations can be daunting, especially when it comes to the intricate setoff rules of the Goods and Services Tax (GST). Understanding the nuances of GST setoff is essential for businesses and individuals alike to optimise tax liabilities and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. In this detailed blog post, we’ll delve into the depths of GST setoff rules, unravelling its complexities and providing practical insights for taxpayers.
Best Compliances Service Provider – Taxgyany
Understanding GST Setoff Rules:
At its core, GST setoff rules govern the mechanism by which taxpayers can offset the tax paid on inputs (input tax) against the tax collected on outputs (output tax). This mechanism is designed to prevent the cascading effect of taxes and ensure that tax is levied only on the value addition at each stage of the supply chain.
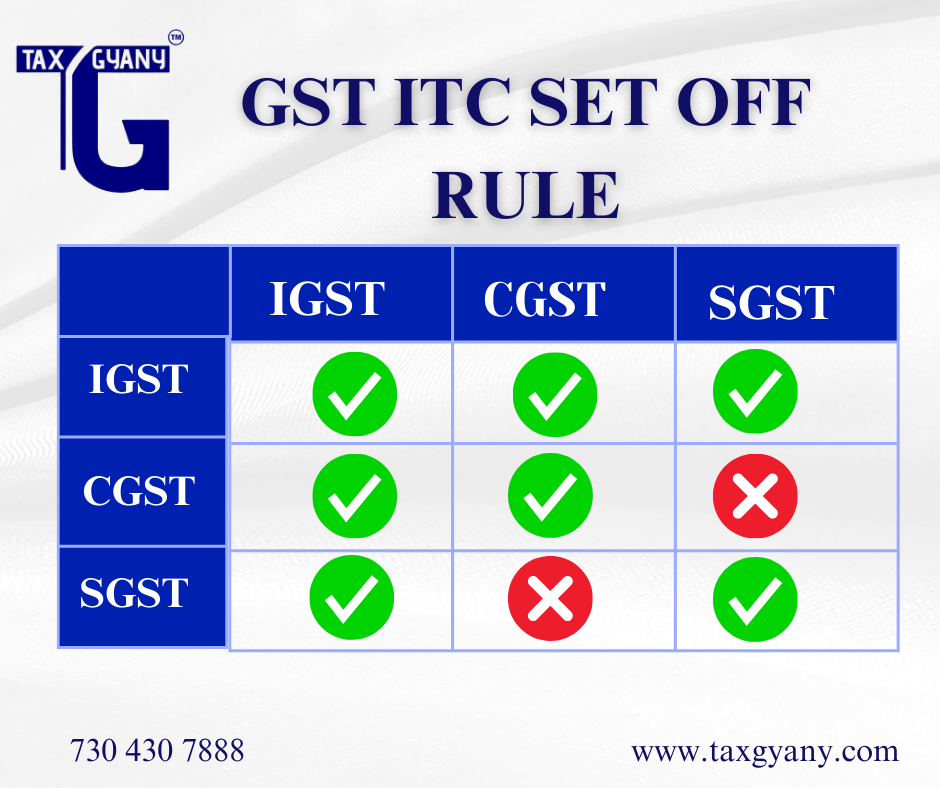
Input Tax Credit (ITC) Explained:
Central to GST setoff rules is the concept of Input Tax Credit (ITC), which allows taxpayers to claim credit for the GST paid on inputs used in the course of business. Eligible inputs include raw materials, goods purchased for resale, and services availed for business purposes. By claiming ITC, taxpayers can effectively reduce their tax liability on outward supplies, thereby lowering their overall tax burden.
Eligibility Criteria for ITC:
To avail of Input Tax Credit, taxpayers must meet certain eligibility criteria. Firstly, they must be registered under GST and possess valid tax invoices or other prescribed documents evidencing the payment of GST on inputs. Additionally, the inputs on which ITC is claimed must be used for business purposes and not for personal consumption. Compliance with these criteria is essential to ensure the legitimate claiming of ITC under GST.
Mechanism of Setoff:
The process of setoff involves reconciling the eligible Input Tax Credit with the output tax liability for a particular tax period. Taxpayers must meticulously maintain records of input tax credits and output tax liabilities to ensure accurate reconciliation. The net tax amount after setoff is then remitted to the government within the stipulated timelines. This reconciliation mechanism is crucial for promoting efficiency and fairness in the GST system.
Maximising Benefits and Ensuring Compliance:
While GST setoff rules offer significant benefits in terms of tax optimization, taxpayers must tread carefully to ensure compliance with statutory requirements. This includes maintaining accurate records, timely filing of returns, and adherence to prescribed procedures for claiming ITC. Failure to comply with these requirements may result in penalties or legal consequences, underscoring the importance of diligent compliance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, mastering GST setoff rules is indispensable for taxpayers seeking to optimise their tax liabilities and ensure compliance with GST regulations. By understanding the fundamentals of Input Tax Credit, navigating the setoff mechanism, and adhering to statutory requirements, taxpayers can unlock the full potential of GST setoff rules in their tax strategy. Stay informed, stay compliant, and harness the power of GST setoff to navigate the complexities of the tax landscape with confidence.
SOURCES:
FOR MORE INFORMATION: https://taxgyany.com/’
